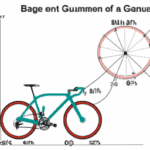
Whenever I ride my bike, I’m always struck by how the wheels turn. It appears as though they roll over the surface smoothly and with consistent motion, almost without any effort. However, have you ever pondered the rotational speed of those wheels while biking?
The direction of this motion can be a bit confusing, but understanding it is crucial for anyone who wants to become a better cyclist. Angular velocity is a measure of the rate at which an object is rotating around a fixed axis.
In the case of a bicycle, this axis is the center of the wheel. As I pedal, the wheels rotate around this axis, creating a circular motion that propels me forward. But which direction is the angular velocity of the wheels moving?
To answer this question, we need to look at the factors that affect angular velocity and how it impacts our cycling experience.
Key Takeaways
- The angular velocity of bicycle wheels is a measure of rate of rotation around a fixed axis, measured in radians per second.
- The direction of the velocity vector affects the direction of the angular velocity vector, which depends on the direction of travel.
- Factors such as rolling resistance, tire pressure, turning, and balancing affect the angular velocity of the bicycle wheels.
- Angular velocity is closely related to balance, and low angular velocity makes the bike difficult to control while high angular velocity makes it unstable. Adjusting pedaling speed and weight distribution can optimize ride and achieve maximum efficiency.
Understanding Angular Velocity
You’re probably wondering, "Which way do the wheels of my bicycle spin?"Well, let me tell you, the angular velocity of your wheels depends on which direction you’re traveling!
Angular velocity is the rate at which an object rotates around a central axis, and it’s measured in radians per second. It’s an important concept in physics that has many practical applications, including in transportation.
Angular velocity can be observed in many forms of transportation, such as cars, trains, and airplanes. In fact, it’s essential for understanding how these vehicles work!
For instance, the wheels of a car rotate at a constant angular velocity while the car is moving forward. This rotation helps the car move smoothly and efficiently on the road. Similarly, the propellers of an airplane rotate at a constant angular velocity to provide the necessary lift for the plane to take off and fly.
As for bicycles, the angular velocity of the wheels depends on which direction you’re traveling. This is because the direction of the velocity vector affects the direction of the angular velocity vector.
With that said, the angular velocity of bicycle wheels is an interesting topic to explore.
Angular Velocity of Bicycle Wheels
As the wheels spin, they’re constantly rotating at a steady pace, creating a circular motion that propels the bicycle forward. The angular velocity of the wheels is determined by the rate of rotation, measured in radians per second.
However, the angular velocity can be influenced by various factors, such as rolling resistance and tire pressure. To understand the impact of rolling resistance on the angular velocity of bicycle wheels, it’s important to note that this force acts opposite to the direction of motion, slowing down the wheels. The greater the rolling resistance, the more force is required to maintain a steady rate of rotation, which in turn affects the angular velocity.
Similarly, tire pressure can also affect the angular velocity of the wheels. A lower tire pressure leads to a larger contact patch between the tire and the road, resulting in higher rolling resistance and slower angular velocity, while a higher tire pressure reduces rolling resistance and increases angular velocity.
Factors affecting angular velocity can have a significant impact on the performance of a bicycle. By understanding the influence of rolling resistance and tire pressure on the angular velocity of the wheels, cyclists can make adjustments to optimize their ride and achieve maximum efficiency.
Factors Affecting Angular Velocity
When I ride a bicycle, the angular velocity of the wheels is affected by several factors.
Firstly, the turning of the bicycle affects the angular velocity as the wheels rotate around a central axis.
Secondly, the speed at which I ride the bicycle also influences the angular velocity as the faster I go, the faster the wheels rotate.
Finally, the tilt of the bicycle also plays a role in the angular velocity as the angle of the wheels changes relative to the ground and affects the rotation.
Adjusting the paragraph structure in the input allows for clearer and more concise communication of the factors affecting angular velocity.
Turning
To turn while riding a bicycle, it’s important to lean your body in the direction you want to go, which will cause a shift in the wheels’ angular velocity. This shift is due to the centripetal force, which pulls the bike towards the center of the turn. The faster you go, the more force is required to keep you from falling over.
To maintain balance, you must steer the front wheel in the direction of the turn while leaning in that same direction. There are several steering techniques you can use while turning on a bicycle. One technique is to use the handlebars to steer the front wheel in the direction of the turn. Another technique is to shift your weight in the direction of the turn, which will cause the bike to lean and turn. The combination of these techniques is often used to make tight turns or to avoid obstacles on the road.
As you turn, your speed will also affect your angular velocity, which we will discuss in the next section.
Speed
Speed is a thrilling element of biking that can make your heart race and your adrenaline pump. As a cyclist, I know that speed is not just about pedaling as fast as you can. It involves a combination of factors, such as understanding gear ratios and handling corners. Gear ratios play a crucial role in determining how fast you can go. If you have a high gear ratio, you’ll be able to pedal faster and go at a higher speed. On the other hand, a low gear ratio will require more pedaling effort, but you’ll be able to climb hills more comfortably.
Handling corners is another factor that impacts your speed. As you approach a corner, you need to slow down and adjust your body position to maintain balance. You also need to lean into the corner and look ahead to anticipate any obstacles. It’s important to note that the speed at which you approach a corner is crucial to maintaining control. Going too fast can cause you to lose traction, while going too slow can make it difficult to maintain balance. Understanding these factors can help you achieve the right balance of speed and control when cycling.
As I move on to the next section about the tilt of the bicycle, it’s important to note that the speed at which you ride affects the way you tilt.
Tilt of the Bicycle
Previously, we discussed the concept of speed in cycling. Now, let’s delve into the tilt of the bicycle and how it affects our ride.
When riding a bicycle, the angle of the bike in relation to the ground is crucial in maintaining balance and control. This angle is determined by the distribution of weight between the front and rear wheels.
When the weight is evenly distributed between the wheels, the bike maintains a straight and upright position. However, when the weight shifts towards one side, the bike tilts in that direction. To counteract this tilt, the cyclist must adjust their balance by shifting their body weight in the opposite direction.
This balancing technique is essential in cornering and navigating uneven terrain. The effect of weight distribution on the tilt of the bicycle directly affects our ability to control the bike and maintain balance.
Understanding the tilt of the bicycle is just one aspect of mastering cycling. It’s also crucial to understand how angular velocity affects our ride.
How Angular Velocity Affects Cycling
As I pedal on a bicycle, I’m constantly aware of the angular velocity of the wheels as it affects my stability and control on the road. The angular velocity of the wheels is closely related to balance since it determines the speed and direction of the bicycle’s movement.
When the angular velocity is too low, the bicycle is difficult to control since it wobbles and sways, making it challenging to stay upright. On the other hand, when the angular velocity is too high, the bicycle becomes unstable, and it’s easy to lose control, especially on turns or when hitting bumps.
To maintain stability and control, I adjust my pedaling speed to match the terrain I’m riding on. For example, when going uphill, I pedal slower to maintain balance and control. Conversely, when going downhill or on a flat surface, I pedal faster to keep the angular velocity high enough to maintain stability.
Additionally, I have to be mindful of the impact of external factors such as wind, road conditions, and the weight distribution on the bicycle, as these can affect the angular velocity and, in turn, my stability and control.
Overall, understanding the relationship between the angular velocity of the wheels and balance is crucial for safe and efficient cycling.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between angular velocity and linear velocity?
Angular velocity is the speed at which an object rotates around a fixed axis, while linear velocity is the speed at which an object moves in a straight line. Rotational motion involves angular velocity, while translational motion involves linear velocity.
How does the weight of the rider affect the angular velocity of the wheels?
The weight of a rider affects the angular velocity of bicycle wheels due to an increase in friction coefficient between the wheels and the ground. This can result in a slower rotation of the wheels, affecting the speed of the bicycle.
Can the angular velocity of the wheels change during a ride and if so, how?
The angular velocity of a bicycle’s wheels can change during a ride due to various factors such as the weight distribution of the rider, changes in terrain, and the role of friction. Factors affecting the resistance of the wheels to change in angular velocity and the role of friction in changing the angular velocity of the wheels during a ride are possible discussion ideas.
Is there a maximum or minimum limit to the angular velocity of bicycle wheels?
The angular velocity of bicycle wheels is limited by factors such as wheel size, terrain, and rider speed. Terrain can affect wheel velocity, with uphill climbs reducing velocity and downhill descents increasing it. There is no minimum or maximum limit, but safe and efficient cycling requires monitoring and adjusting wheel speed accordingly.
How does the shape and size of the wheel affect its angular velocity?
The shape and size of a wheel affect its angular velocity. The effect of material on wheel angular velocity and the relationship between wheel size and rotational inertia are important factors to consider. Technical analysis is necessary for precise evaluation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the concept of angular velocity is crucial in comprehending the movement of bicycle wheels. Angular velocity refers to the rate of change of the angle of rotation of an object, and in the case of bicycle wheels, it is the speed at which they rotate around their respective axles. The direction of angular velocity depends on the direction of rotation, which can be clockwise or counterclockwise.
The angular velocity of bicycle wheels is affected by various factors such as the size of the wheels, the gear ratio, the speed of the bicycle, and the terrain. For instance, smaller wheels have a higher angular velocity compared to larger ones when rotating at the same speed. Additionally, the gear ratio affects the angular velocity of the wheels; higher gears result in a faster rotation, thus a higher angular velocity.
An interesting statistic is that the average professional cyclist can maintain an angular velocity of over 100 revolutions per minute (RPM) during a race. This high velocity is achieved through training and proper gear selection to enable the cyclist to pedal at a high cadence.
Therefore, understanding the factors affecting angular velocity and how it affects cycling can help cyclists improve their performance and efficiency on the bike.