As a cyclist, grasping the concept of gear ratio on my bicycle plays a crucial role in enhancing my performance. Although it may initially appear complicated and overwhelming, the process of figuring out the gear ratio becomes straightforward once you get a handle on the fundamental principles.
Gear ratio refers to the relationship between the number of teeth on the front and rear gears of your bicycle. This ratio determines how much leverage you have when pedaling, and can greatly affect your speed and efficiency on the road.
By understanding how to calculate gear ratio, you can make informed decisions about which gears to use in different situations and ultimately improve your cycling performance.
So, let’s dive in and explore how to calculate gear ratio on a bicycle.
Key Takeaways
- Gear ratio is the relationship between the number of teeth on the front and rear gears of a bicycle, which affects speed and efficiency.
- To calculate gear ratio, count teeth on the chainring (front gear) and cassette (rear gear) and divide.
- Chainring selection plays a crucial role in gear ratio optimization and determines the gear range of the bicycle.
- Choosing the appropriate gear ratio based on terrain, fitness level, bike weight, and riding style can maximize efficiency and minimize fatigue.
Understanding the Basics of Gear Ratio
You’ll understand how the gear ratio works by visualizing it as the number of times the rear wheel rotates in relation to the number of times the pedals rotate. The ratio between these two numbers is what determines the power and speed of your bike.
The gear ratio is usually expressed as a fraction or a decimal, with the first number representing the number of teeth on the chainring (the front gear) and the second number representing the number of teeth on the cassette (the rear gear).
Understanding the benefits of gear ratio is crucial for any cyclist. By changing the gear ratio, you can adjust the resistance on the pedals and make riding easier or harder.
Gear ratio and terrain are closely related; for example, a low gear ratio is ideal for uphill climbs, while a high gear ratio is better for flat or downhill terrain. With this knowledge, you can optimize your gear ratio for any ride and enjoy a smoother, more efficient cycling experience.
Now, let’s move on to how to calculate gear ratio.
How to Calculate Gear Ratio
To calculate the gear ratio on my bicycle, I need to determine the number of teeth on the chainring and cassette/freewheel.
First, I have to count the number of teeth on the chainring, which is the larger ring attached to the pedals.
Second, I have to count the number of teeth on the cassette/freewheel, which is the cluster of gears on the rear wheel.
Finally, I have to divide the number of teeth on the chainring by the number of teeth on the cassette/freewheel to get the gear ratio.
Determine Chainring Teeth
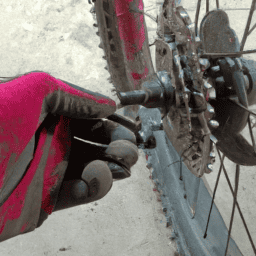
If you’ve already counted the teeth on your cassette, the next step is to take a look at your chainring and count the teeth there as well. Chainring selection plays a crucial role in gear ratio optimization, so it’s important to pay attention to this step.
The chainring is the front gear that’s attached to the pedal crank and it’s usually larger than the cassette gears. Counting the teeth on the chainring will help you determine the gear ratio that you’ll be using on your bike.
To count the teeth on your chainring, you’ll need to visually inspect the front of your bike where the pedals are located. Look for the chainring and count the number of teeth that are visible. It’s important to double-check your count to make sure you have an accurate number.
Once you have the number of teeth on your chainring, you’ll be able to move on to the next step of determining the teeth on your cassette/freewheel.
Determine Cassette/Freewheel Teeth
Now that you’ve determined the teeth on your chainring, take a look at your cassette or freewheel to count the teeth there as well.
The cassette or freewheel is the set of gears at the rear wheel of the bike. Count the number of teeth on each gear, starting with the smallest one, and moving towards the largest.
The teeth measurement is essential to determine the gear ratio of the bicycle. The teeth measurement on the cassette or freewheel, when combined with the chainring, determines the gear range of the bicycle.
The gear range refers to the number of gear combinations that are available on the bike. The gear range can be used to determine how easy or hard it will be to pedal the bike up hills or to go faster on flat ground.
With this information, we can move on to the next step, which is to calculate the gear ratio of the bicycle by dividing the chainring teeth by cassette/freewheel teeth.
Divide Chainring Teeth by Cassette/Freewheel Teeth
Once you’ve counted the teeth on both the chainring and cassette/freewheel, simply divide the numbers to calculate the gear ratio. This will give you an idea of how many times the rear wheel will rotate for every single rotation of the pedals. To make sure you’re doing it right, follow these steps:
- Count the teeth on the chainring and write down the number.
- Count the teeth on the cassette/freewheel and write down the number.
- Divide the number of teeth on the chainring by the number of teeth on the cassette/freewheel.
- Round the number to the nearest hundredth.
Common mistakes when calculating the gear ratio include forgetting to count the teeth on either the chainring or cassette/freewheel, or dividing the numbers in the wrong order. It’s important to double-check your calculations to make sure you’re getting an accurate result.
Additionally, there are alternative methods to calculate gear ratio, such as using a gear ratio calculator or measuring the distance traveled by the bike for every rotation of the pedals.
Knowing the gear ratio can help you optimize your performance on the bike, but it’s not the only factor to consider. In the next section, we’ll explore how to use the gear ratio in conjunction with other aspects of cycling to improve your ride.
Using Gear Ratio to Optimize Performance
To optimize your performance on a bicycle, you’ll want to use the gear ratio to find the most efficient combination of gears for your desired speed and terrain. A high gear ratio will give you more speed, while a lower gear ratio will give you more power for climbing hills. It’s important to find the right balance between speed and power to avoid exerting too much effort and causing muscle fatigue.
Optimizing cadence is also crucial in finding the right gear ratio. Cadence refers to the rate at which you pedal and is measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). A cadence of around 80-100 RPM is considered ideal for most riders. By adjusting your gear ratio, you can maintain a consistent cadence, which will help you ride more efficiently and reduce the risk of injury.
The importance of gear ratio in hill climbing cannot be overstated, as it can make a huge difference in your ability to ascend steep inclines. By selecting the gear with the appropriate ratio, you can maintain a steady cadence and avoid burning out your leg muscles before reaching the top.
Understanding how gear ratios affect your bike’s performance is essential for any cyclist. The next step is to explore the relationship between gear ratio and bike components.
Gear Ratio and Bike Components
Maximizing your bike’s performance is possible by understanding how gear ratios relate to the components of your bike. A bike’s gear ratio is the ratio of the number of teeth on the front chainring to the number of teeth on the rear cassette. This ratio determines how much effort is required to turn the pedals and how fast the bike goes.
It is important to maintain the gear ratio of your bike to ensure optimal performance. Gear ratio maintenance involves keeping the chain clean and lubricated, regularly inspecting and replacing worn components, and adjusting the derailleur as needed.
Here are four factors to consider when choosing the right gear ratio for different terrains:
-
Terrain: The gear ratio you choose should be based on the type of terrain you will be riding on. For example, a lower gear ratio is ideal for climbing hills, while a higher gear ratio is better suited for flat roads.
-
Fitness level: Your fitness level will also play a role in determining the gear ratio you should use. If you’re a beginner, you may want to start with a lower gear ratio to avoid straining your muscles. As you become more experienced, you can gradually increase the gear ratio to challenge yourself.
-
Bike weight: The weight of your bike will also affect the gear ratio you should use. A heavier bike will require a lower gear ratio to make it easier to pedal, while a lighter bike can handle a higher gear ratio.
-
Riding style: Your riding style will also influence the gear ratio you should use. If you prefer to ride at a faster pace, a higher gear ratio will be more suitable. On the other hand, if you prefer a more leisurely pace, a lower gear ratio will be more comfortable.
Understanding the relationship between gear ratio and bike components is essential for maximizing your bike’s performance. To choose the right gear ratio, consider factors such as terrain, fitness level, bike weight, and riding style.
Tips for Choosing the Right Gear Ratio
In the previous subtopic, we learned about the concept of gear ratio and how it relates to the different components of a bicycle. Now, let’s delve deeper into the topic and discuss some tips for choosing the right gear ratio.
The gear ratio on a bicycle is determined by the number of teeth on the front chainring and the rear cassette. The right gear ratio can make a huge difference in your cycling experience, especially when it comes to tackling different types of terrain. There are several factors that can affect your gear ratio, such as your fitness level, the gradient of the terrain, and the type of cycling you plan to do. To help you choose the right gear ratio, let’s take a look at this table that shows the recommended gear ratios for different types of terrain:
| Terrain Type | Recommended Gear Ratio |
|---|---|
| Flat roads | 50/16 or 50/15 |
| Rolling hills | 50/19 or 50/21 |
| Steep hills | 34/28 or 34/30 |
| Off-road trails | 32/36 or 32/40 |
| Uphill climbs | 34/28 or 34/30 |
By selecting the appropriate gear ratio for the terrain, you can maximize your efficiency and minimize your fatigue. Changing your gear ratio can also provide several benefits, such as a smoother ride, better control over your speed, and increased power output. So, before you hit the road or trail, take some time to consider the factors that may affect your gear ratio and choose the one that best suits your cycling needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do gear ratios affect a cyclist’s speed and power output?
To optimize speed and power output, a cyclist must strategically select their gear ratios. Gear ratio optimization involves finding the perfect balance between the force applied to the pedals and the speed at which the cyclist wants to travel.
Can gear ratios be adjusted while riding, or do they need to be set before starting a ride?
While riding, gear ratios can be adjusted on the go using shifters. However, it is recommended to make pre-ride adjustments to ensure optimal performance and prevent damage to the drivetrain.
Are there any downsides to using a high gear ratio, such as increased wear on bike components?
Using a high gear ratio can lead to increased maintenance due to increased stress on bike components. It also has the potential to cause muscle strain for the rider. It’s important to find the right balance between gear ratio and rider comfort.
How does the weight of the cyclist affect the optimal gear ratio for a particular ride?
As a cyclist, my weight impacts the optimal gear selection for a particular ride. A heavier cyclist may require a lower gear ratio to maintain a comfortable cadence and prevent excessive strain on the muscles.
Is it necessary to have a deep understanding of gear ratios in order to enjoy cycling as a hobby or sport?
Understanding gear ratios is crucial for competitive cycling, but less so for recreational riders. Choosing the right gear ratio depends on terrain and riding style, with lower ratios for hills and higher ratios for speed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the gear ratio on your bicycle is crucial to optimizing your cycling performance. By calculating the gear ratio, you can determine the relationship between the number of teeth on the front and rear gears, which in turn affects your speed and power output.
Gear ratio can also be used to adjust for different terrain and riding styles. Just like a chef carefully selecting the right ingredients for a recipe, choosing the right gear ratio for your bike requires careful consideration of your personal preferences and riding goals.
With the proper gear ratio, you can smoothly shift gears and effortlessly conquer hills and valleys. So, take the time to calculate your gear ratio and experiment with different combinations to find the perfect setup for your cycling adventures.
Happy riding!