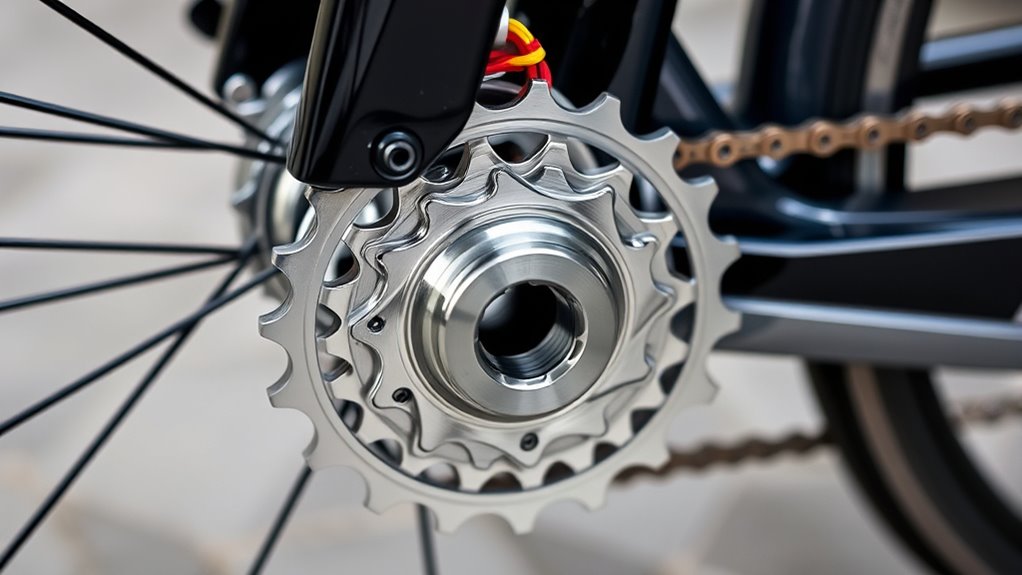
Gearing systems on your road bicycle control pedal effort and speed by changing how power is transferred from your legs to the wheels. They involve front chainrings and rear cassettes, which work together to adjust gearing ratios, making pedaling easier or harder depending on terrain. Understanding gear ratios and gear inches helps you choose the right setup for different rides. Keep exploring to discover how to shift smoothly and optimize your riding experience.
Key Takeaways
- Gearing systems control pedaling effort and speed by combining front chainrings and rear cassettes for various terrain demands.
- Gear ratios, determined by teeth count, influence pedaling difficulty and riding speed, with gear inches indicating overall gearing.
- Mechanical and electronic shifting systems differ in operation, maintenance, and ease of use, affecting performance and cost.
- Proper shifting techniques, such as smooth, one-gear changes and avoiding cross-chaining, extend drivetrain life and improve efficiency.
- Choosing the right gear setup depends on riding style, terrain, and preferences, optimizing comfort and performance.
What Are Gears on a Bike?
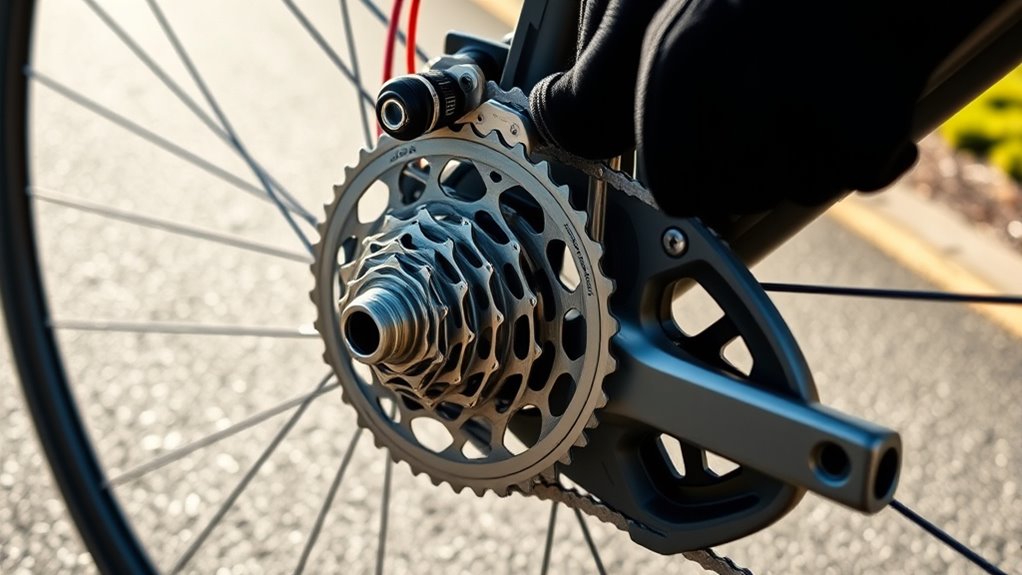

Gears on a bike are mechanisms that help you control how hard or easy it is to pedal. They consist of gears, including the front chainring and rear cassette, which work together to change the gear ratios. The number of teeth on each gear determines how much resistance you face when pedaling. A derailleur moves the chain across different sprockets and chainrings, allowing you to shift gears smoothly. This gear system offers various gear combinations, so you can find the right balance between effort and speed. When you shift gears, you’re adjusting the gear ratios to match terrain and riding conditions. Understanding how gears, chainrings, and the rear cassette work together helps you optimize your pedaling efficiency and ride more comfortably. Additionally, a well-designed gearing system can improve your overall performance and comfort on diverse terrains. Recognizing the importance of gear ratios can assist in selecting the right gear for different cycling scenarios. Modern gearing systems are also engineered to provide seamless shifting, enhancing the overall riding experience. Furthermore, advancements in derailleur technology have contributed to smoother and more reliable gear changes. A good understanding of gear adjustments can help prevent issues like chain slipping or skipping during rides.
How Do Gearing Systems Work in Road Bicycles?

When you shift gears on a road bicycle, you’re changing the gear ratio, which affects how hard or easy it is to pedal and how fast you go. The derailleur moves the chain between different sprockets and chainrings, allowing you to match your effort to the terrain. Proper shifting involves anticipating terrain and smoothly switching to maintain efficiency and prevent drivetrain issues. Additionally, understanding how gear ratios work can help optimize your riding performance and comfort. The tuning of your drivetrain components, including the derailleur and shifters, plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless gear changes. To achieve optimal performance, it’s also important to keep your drivetrain well maintained and clean. Regular inspection and cleaning of components like the chain and sprockets ensure that gear shifts remain smooth and reliable, especially as components wear over time.
Gear Ratios and Effort
Understanding how gear ratios impact effort is key to mastering road cycling. The gear ratio, calculated by dividing the front chainring size by the rear sprocket size, directly affects your pedaling effort. Higher gear ratios, with larger chainrings or smaller sprockets, deliver more speed but require more effort. Lower ratios, achieved with smaller chainrings or larger sprockets, make pedaling easier, especially on inclines. Proper gear combinations optimize your mechanical advantage and help maintain a consistent cadence. Here’s a quick overview:
| Gear Ratio | Effect | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|
| High gear | Increased effort | Flat terrain, high speed |
| Low gear | Reduced effort | Climbing, headwinds |
| Large chainring | Higher gear ratio | Sprinting, fast riding |
| Small sprocket | Higher gear ratio | Speed on flat roads |
| Small chainring | Lower gear ratio | Climbing, rough terrain |
Shifting Mechanics and Techniques
Shifting mechanics in road bicycles rely on derailleur systems that move the chain between front chainrings and rear sprockets, allowing you to change gears according to terrain and riding needs. To shift, you push the shifter paddles or levers, which actuate the derailleur mechanisms. Mechanical shifters use cables that pull or release to guide the derailleur, while electronic shifters rely on motors for precise gear changes. Proper technique involves pedaling steadily and shifting gradually across gears to maintain chain tension and guarantee a smooth transition. Anticipate terrain changes by shifting before stopping or accelerating. Avoid cross-chaining to prevent drivetrain wear. Effective shifting maintains ideal gear ratio, minimizes chain noise, and guarantees efficient power transfer.
Understanding Gear Ratios and Gear Inches

Gearing systems on road bicycles rely on the relationship between the number of teeth on the front chainring and the rear sprocket, known as the gear ratio. This ratio determines how many wheel revolutions occur per pedal stroke. To visualize:
- A large front chainring paired with a small rear sprocket yields a high gear ratio, increasing speed but demanding more pedaling effort.
- A smaller front chainring with a larger rear sprocket results in a lower gear ratio, making climbing easier.
- Gear inches, calculated by multiplying the gear ratio by wheel diameter, measure the effective wheel size and riding effort. Higher gear inches mean faster rides but more effort, while lower gear inches favor easier pedaling.
- Understanding gear ratios and gear inches helps you choose the ideal gear for terrain and riding style. Additionally, familiarity with art theory can enhance your appreciation of bicycle design as an art form that combines function and aesthetics, emphasizing the importance of design principles in creating efficient and appealing bicycles. Recognizing the role of manufacturing techniques in bicycle construction also deepens your understanding of how quality components contribute to overall performance. Being aware of regulatory guidelines, such as those from the IRS, ensures you select gear setups that comply with safety standards and best practices.
Different Types of Gearing Setups for Road Bikes

When choosing a gearing setup, you’ll want to think about whether mechanical or electronic shifting best suits your riding style. Single gear options simplify maintenance, while multiple gears offer more versatility for varied terrains. Understanding these differences helps you pick the right system for your needs. Additionally, some gearing systems incorporate essential oils to help riders stay relaxed and focused during long rides. Selecting the appropriate gearing system also involves considering gear ratios, which determine how easy or hard it is to pedal at different speeds and inclines. Moreover, knowing about maintenance requirements can influence your choice, as different systems may demand varying levels of upkeep to ensure optimal performance. For example, gear ratio selection can significantly impact your overall riding efficiency and comfort, especially when considering drive train compatibility with your bike’s components.
Mechanical vs. Electronic Shifting
You have two main options for changing gears on a road bike: mechanical and electronic systems. Mechanical shifting uses cables and levers to move derailleurs, with brands like Shimano STI, Campagnolo Ergo, and SRAM DoubleTap. When you make gear changes, cable tension adjusts the derailleur gears, but it requires manual maintenance. Electronic shifting replaces cables with battery-powered motors, offering precise, instant gear changes via Shimano Di2, Campagnolo EPS, or SRAM AXS systems. Imagine:
- Smooth, effortless gear changes with electronic shifting’s shift modes.
- Mechanical shifting needing manual cable tension adjustments.
- Electronic systems automatically trimming derailleur gears for a precise gear every time.
Choosing depends on your preference for maintenance, budget, and desire for convenience.
Single vs. Multiple Gears
Road bike setups range from simple single-gear systems to complex multi-gear configurations, each serving different riding needs. A single gear offers only one gear ratio, making it easy to maintain and operate, ideal for flat terrain and urban commuting. Multiple gears, with varying gear ratios, provide more gear options through different chainrings and a wide-range cassette, allowing you to adapt to diverse terrains. Double chainring setups, like 52/36 or 50/34, balance speed and climbing ability, while triples with three chainrings, such as 52/39/30, deliver a broad gear range for steep climbs or loaded touring. Modern trends favor 1x drivetrains, combining simplicity with enough gear options for most road riding conditions, offering a streamlined gear setup with fewer components. Additionally, the choice of gearing system can be influenced by the diverse designs available to match specific riding styles and preferences. Understanding the cost-effectiveness of different gear setups can help riders select options that fit their budget and riding goals.
When and How to Shift Gears Effectively

Shifting gears at the right moments helps maintain a smooth and efficient ride. To do this effectively:
- Anticipate terrain changes and shift to lower gears before climbing or higher gears before descending, keeping your cadence steady.
- Shift one gear at a time, pedaling steadily to allow the derailleur to move smoothly and the chain to align properly on the sprocket or chainring.
- Avoid cross-chaining by staying within ideal gear ratios, which reduces strain on the drivetrain and prevents wear.
Exploring Front Gears, Rear Cassettes, and Their Roles
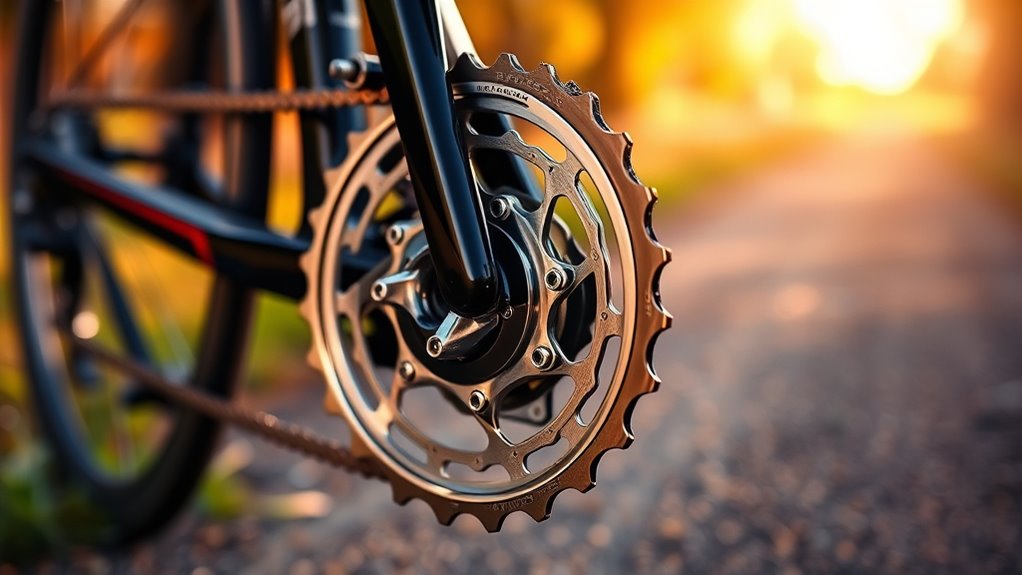

Understanding the roles of front gears and rear cassettes is essential for optimizing your bike’s performance. The front gears, or chainrings, are mounted on the crankset and come in various configurations like single, double, or triple, influencing your gear setup. The rear cassette consists of sprockets that work with the chain to provide different gear ratios, affecting pedaling effort and speed. A higher gear ratio, achieved with larger chainrings and smaller sprockets, boosts speed on flat terrain, while lower ratios help with climbing. Your gear range depends on the combination of front gears and rear sprockets, and effective gear shifting involves selecting appropriate gear combinations before terrain changes. This balance improves efficiency, cadence, and overall riding experience.
Tips for Choosing the Right Gear for Your Riding Needs
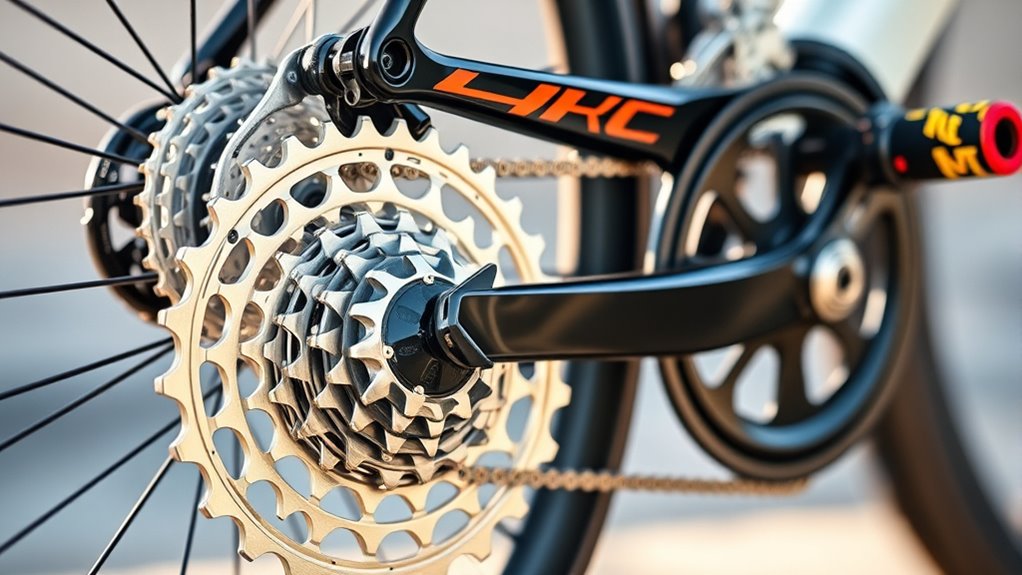

Choosing the right gear depends on matching your bike’s setup to your riding terrain and style. To optimize your gear selection, consider terrain and desired cadence. For steep hills, select lower gear ratios like 34/28 or an 11-34 cassette to keep pedaling smooth. For flat sprints, higher gears such as 53/11 provide speed. Use a gear calculator to determine appropriate gear inches and ratios, ensuring efficient pedaling. Focus on a gear setup—like a compact crankset—that suits your goals, whether climbing, racing, or commuting. When shifting, anticipate terrain changes and shift proactively to avoid drivetrain wear or chain slip. Keep your cadence between 70 and 100 rpm by adjusting gears early, maintaining smooth, efficient riding.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Understand Bicycle Gearing Ratios?
When you want to understand bicycle gearing ratios, focus on how the front chainring and rear sprocket work together. Divide the number of teeth on the front by those on the rear to get the ratio. Higher ratios mean more speed but require more effort. Lower ratios make pedaling easier, especially uphill. Knowing this helps you pick the right gear for your terrain, balancing effort and speed effectively.
What Is the Best Gearing for Road Cycling?
When it comes to the best gearing for road cycling, you need to strike a balance, don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Opt for a compact crankset like 52/36T combined with an 11-30 cassette; this setup handles both flat stretches and climbs with ease. Modern 11- or 12-speed groupsets give you fine-tuned shifts, helping you keep your cadence steady and ride efficiently on any terrain.
How to Use Road Bike Gears Correctly?
To use your road bike gears correctly, shift gradually before you hit hills or corners to keep things smooth. Use lower gears for climbs and against the wind to make pedaling easier, and switch to higher gears when you want to go faster downhill or accelerate. Always pedal while shifting, and avoid cross-chaining to prevent wear. This keeps your drivetrain healthy and riding efficient.
What Gear Ratio Is Best for Uphill?
When you’re climbing uphill, you want a low gear ratio to make pedaling easier. Aim for a ratio around 3:1 or lower, like 34/11 or 36/11. This reduces resistance and helps you maintain a steady cadence between 70-90 rpm. Using a compact or triple crankset with a wide-range cassette, such as 11-36 or 11-40, gives you the best gears for steep inclines.
Conclusion
Now that you understand how gearing systems work, imagine yourself effortlessly shifting through gears on a challenging climb or smooth descent. The right gear choice transforms your ride, making every pedal stroke smoother and more efficient. But the true test is in your hands—will you master the timing and technique to release your bike’s full potential? The journey to seamless shifting begins now—are you ready to take it?